Table of Contents
ToggleCommercial compliance programs serve as the foundation of organizational integrity, ensuring adherence to all applicable rules and regulations specifically related to the company’s commercial activities.
From the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) compliance mandates to the Office of Inspector General’s (OIG) enforcement-centric stance on third-party engagements, commercial compliance programs are designed not just for regulatory reporting but for fostering a culture of compliance throughout the organization.
Gone are the days when compliance was synonymous with filing Open Payments reports and other regulatory documentation.
Today, it’s about proactive risk mitigation and leveraging cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, data science, and machine learning to effectively and efficiently monitor commercial practices.
It has become a dynamic process to ensure ethical, compliant, and legally responsible conduct, especially in an industry where the stakes are life-altering.
What is a Commercial Compliance Program?
A commercial compliance program for a life sciences company is a set of policies, procedures, and practices designed to ensure that the company’s commercial activities comply with applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards.
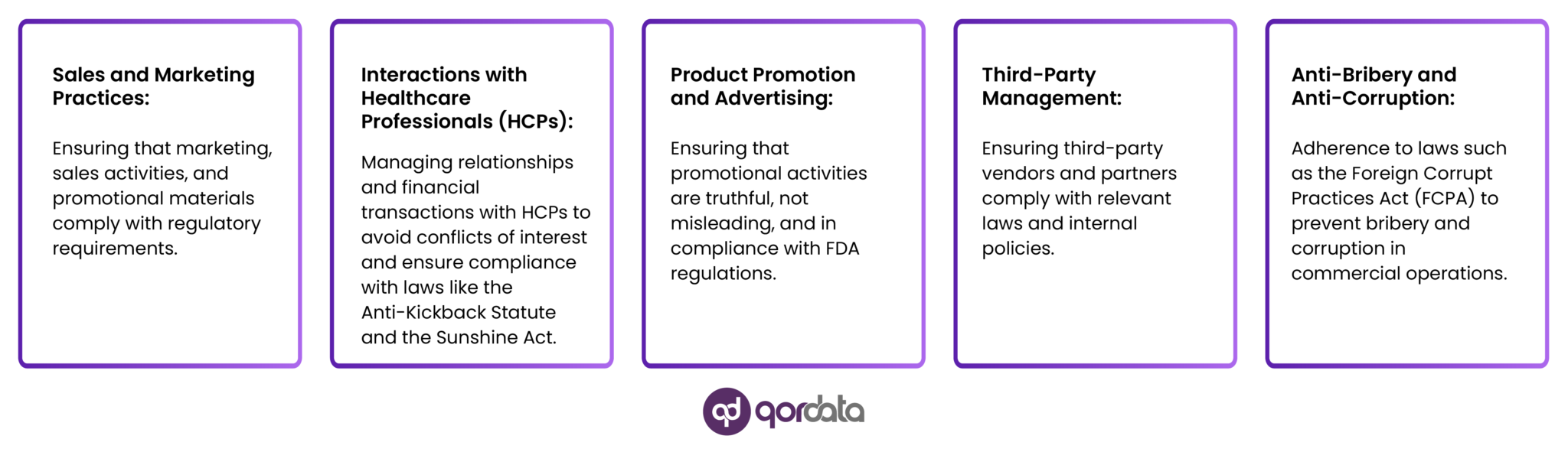
The program typically includes measures to identify, assess, and manage compliance risks related to:
It may also include monitoring, auditing, and reporting mechanisms to detect and correct compliance violations.
A robust commercial compliance program can help the company avoid legal and reputational risks, protect patient safety and privacy, and promote a culture of integrity and accountability.
Why Have a Commercial Compliance Program?
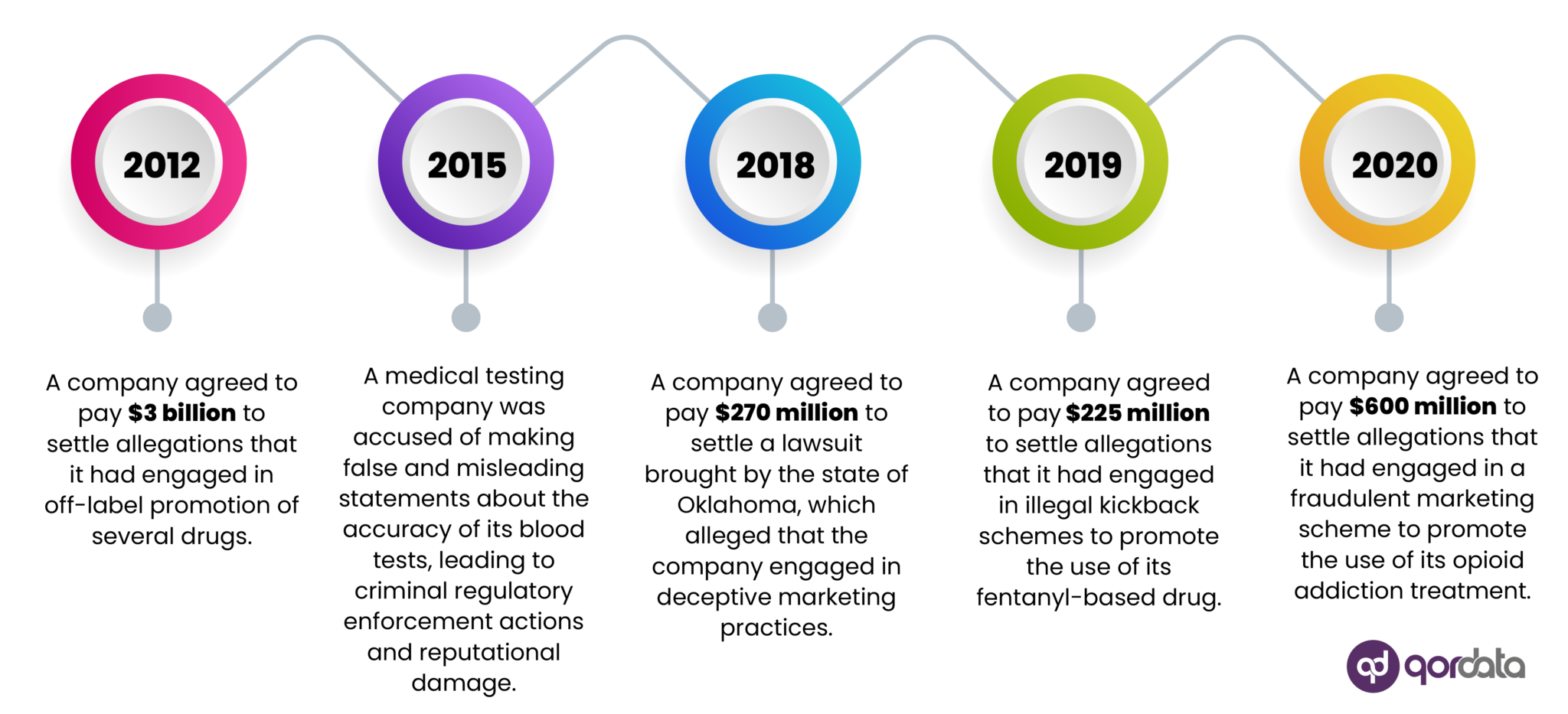
Over the years, state, federal, and international prosecutors have intensified their enforcement actions against non-compliance, often imposing substantial monetary penalties.
The most effective way for a company to avoid such penalties is to demonstrate that it has genuinely complied with commercial compliance laws, even if a few individuals (employees or third parties working on the company’s behalf) violate these laws.
Commercial compliance programs generate the documentation and evidence to prove these efforts to prosecutors.
For instance, if employees are trained that bribing healthcare professionals (HCPs) or government officials violates the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA), and the company can provide evidence such as training records and email documentation, it can show prosecutors: “Here are our training records. You can see that John has received training 12 times over 10 years. Despite this, here are our email records of him conspiring to violate the FCPA.”
This kind of documentation makes it more likely that prosecutors will target the individual wrongdoer rather than sanction the company.
On the other hand, failure to implement an effective compliance program is akin to telling prosecutors, “John did what? He bribed whom? We had no idea. Our bad.” Such a response is unlikely to help the company avoid penalties.
An effective commercial compliance program demonstrates that your organization is aware of the applicable rules and laws and takes reasonable, effective steps to adhere to them.
This proactive approach mitigates legal risks and fosters a culture of compliance, which is essential for long-term success and integrity in the life sciences industry.
Building a Commercial Compliance Program
Establishing the infrastructure of an effective commercial compliance program is critical, including the resources necessary to build and implement the program across the organization.
This infrastructure includes:
- Board of Directors Resolution
- Formally establish and recognize the corporate compliance program through a Board of Directors resolution. This step demonstrates the Board’s commitment to compliance and fulfills its fiduciary obligations to oversee the commercial compliance program.
- Corporate Code of Conduct and Ethics
- Draft or revise a corporate code of conduct and ethics tailored for commercial life sciences companies. While many companies have a code of conduct that addresses securities requirements, these may lack essential health regulatory provisions for a commercial life sciences organization.
- Charters for Compliance Program and Committee
- Develop charters for the compliance program and compliance committee. These charters should document the compliance program’s composition, roles, responsibilities, and resources.
- The Role Of A Chief Compliance Officer
- Define the chief compliance officer’s job description and reporting structure to ensure clarity in roles and responsibilities.
Key Compliance Resources
- Compliance Policies and Procedures
Adopt compliance policies and procedures to establish clear compliance parameters.
- Compliance Training
Provide comprehensive compliance training to educate employees, contractors, and vendors on compliance expectations and standards.
- Compliance Reporting Mechanism
Implement a mechanism for reporting compliance concerns, ensuring it is accessible and confidential.
- Compliance Monitoring and Auditing
Conduct regular compliance monitoring and auditing activities to identify and address potential compliance issues proactively.
- Compliance Investigations
Conduct thorough investigations to determine the root cause of compliance issues and implement corrective measures.
- Disciplinary and Corrective Measures
Take appropriate disciplinary and corrective actions to address and deter compliance violations, ensuring accountability.
List of Commercial Compliance Policies And Procedures You Should Develop
The compliance policies and procedures that a life sciences company should develop and implement will depend on various factors, including the specific business activities that the company conducts. These activities necessitate establishing compliance parameters to minimize risks.
Companies should identify areas of non-compliance and develop, monitor, maintain, and update policies and procedures relevant to such risks.
Key policies and procedures to consider include:
- Gifts, Meals, and Entertainment
- Policies to regulate the provision of gifts, meals, and entertainment to HCPs and other stakeholders to prevent undue influence.
- Interactions with Healthcare Professionals
- Guidelines governing interactions with HCPs to ensure compliance with anti-kickback statutes and other regulations.
- Interactions Between Commercial and Medical Employees
- Procedures to manage and monitor interactions between commercial and medical employees to avoid conflicts of interest.
- Policies for ensuring that all payments and transfers of value to HCPs are consistent with established fair market values.
- Promotional Speaker Programs and Engaging HCP Speakers
- Guidelines for conducting promotional speaker programs and engaging HCP speakers, including contracting and compensation.
- Promotional Communications and Review Committee
- Procedures for reviewing and approving promotional communications to ensure they are accurate, balanced, and compliant with regulatory standards.
- Booths, Exhibits, and Displays
- Policies governing the setup and conduct of booths, exhibits, and displays at conferences and events to ensure compliance.
- Charitable Donations, Grants, Fellowships, Sponsorships, and Corporate Memberships
- Guidelines for making charitable donations, grants, fellowships, sponsorships, and corporate memberships to ensure they are made for legitimate purposes and do not constitute improper inducements.
- Advisory Boards and Consultants
- Procedures for engaging and compensating advisory boards and consultants, ensuring transparency and compliance with relevant laws.
- Field Call Plans
- Policies outlining the appropriate conduct and procedures for field sales representatives when visiting HCPs and other stakeholders.
- Field Compensation Plans
- Guidelines for developing and managing compensation plans for field sales representatives.
- Company-Conducted Product Training
- Procedures for conducting product training and demonstrations to ensure they are accurate, compliant, and educational.
- Product Samples, Coupons, and Vouchers
- Policies regulating the distribution of product samples, coupons, and vouchers.
- Transparency, Licensure, and Marketing Compliance
- Guidelines for maintaining transparency in business practices, ensuring proper licensure, and complying with marketing regulations.
- Medical Information Requests and Communications
- Procedures for responding to requests and communicating medical information to ensure accuracy and compliance.
- Adverse Event Reporting, Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies
- Policies for reporting adverse events and managing risk evaluation and mitigation strategies to ensure patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
There are several items that a robust commercial compliance program will need to consider as the life sciences regulatory landscape evolves. The key to success for compliance officers is to realize that a compliance program is never done or completed. It requires continuous review and updates to remain fresh, relevant, and effective.
qordata helps life sciences companies overcome increasing Board and regulatory scrutiny, adhere to all applicable rules and regulations, minimize risks, and assure compliance at all levels.
Our AI-powered Data-Driven Compliance Platform consists of all the essential solutions, training, and services, serving as a one-window platform to ensure your compliance program is well-designed and effective.
The platform leverages Artificial Intelligence such as Computer Vision, OCR, Machine Learning, Data Sciences, and Generative AI to solve life sciences compliance challenges through technology.
It is a global platform that empowers life sciences compliance teams to get a holistic view of all the risks across the organization. It offers coverage of the seven elements of an effective compliance program while adapting seamlessly to your existing processes.
Other Relevant Read: